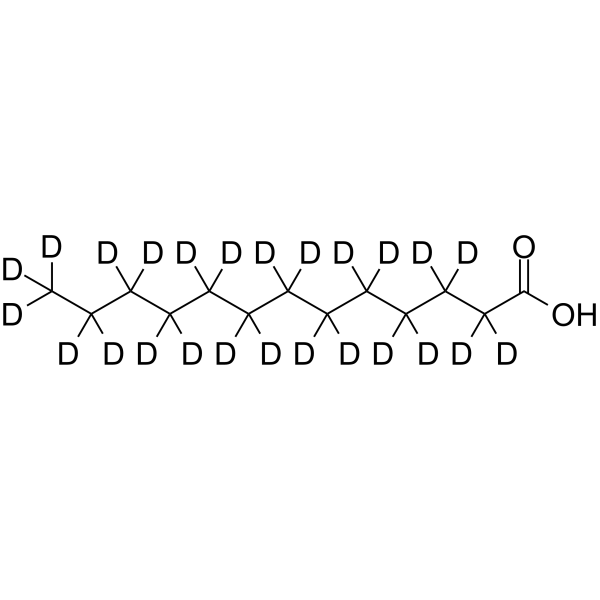Search Result
Results for "
bacterial biofilm
" in MedChemExpress (MCE) Product Catalog:
4
Biochemical Assay Reagents
10
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Areas |
Chemical Structure |
-
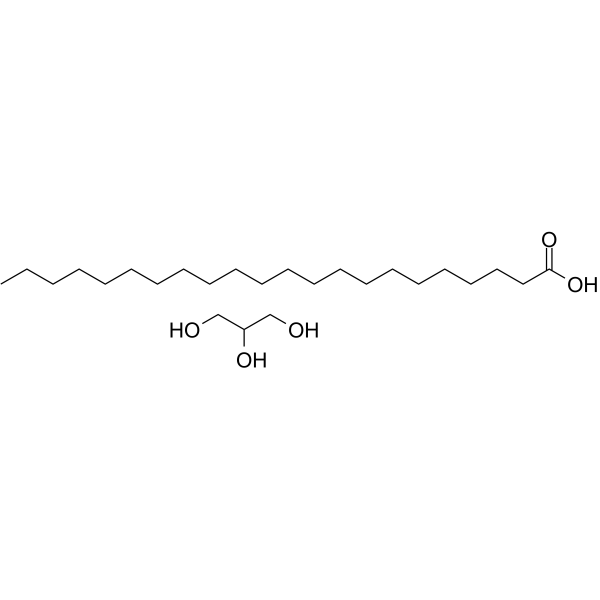
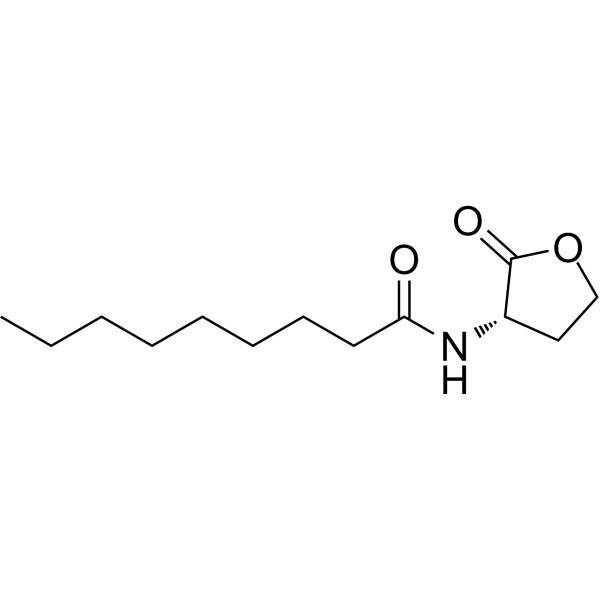
- HY-20349
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Monobehenin, an bacterial biofilm formation inhibitor, has strong inhibitory activity toward bacterial biofilm formation of S. mutans, X. oryzae, and Y. enterocolitica in a strain specific manner .
|
-
-
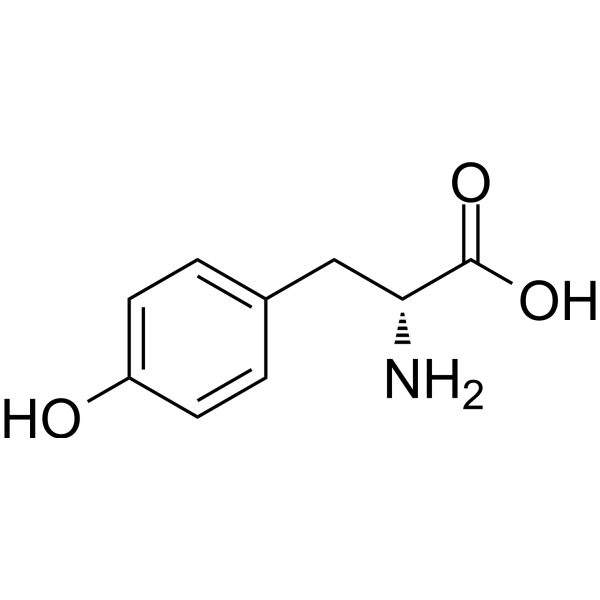
- HY-Y0444
-
|
|
Tyrosinase
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
D-Tyrosine is the D-isomer of tyrosine. D-Tyrosine negatively regulates melanin synthesis by inhibiting tyrosinase activity. D-Tyrosine inhibits biofilm formation and trigger the self-dispersal of biofilms without suppressing bacterial growth .
|
-
-
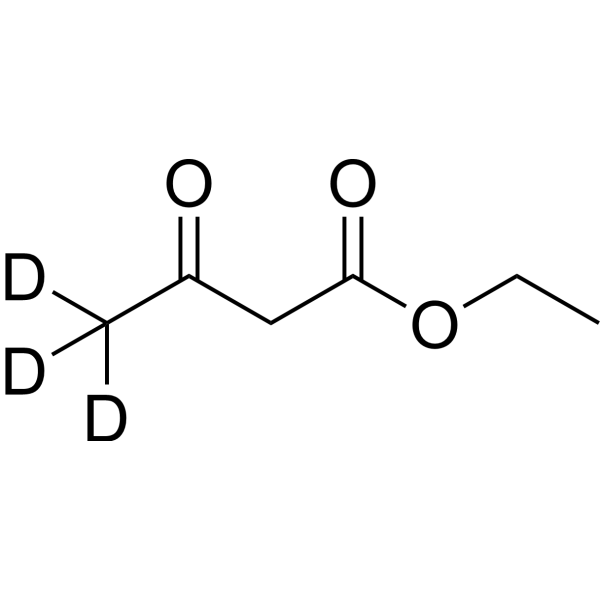
- HY-Y1093S4
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
Ethyl acetoacetate-d3 is the deuterium labeled Ethyl acetoacetate. Ethyl acetoacetate (Ethyl acetylacetate) is an ester widely used as an intermediate in the synthesis of many varieties of compounds[1][2][3]. Ethyl acetoacetate is an inhibitor of bacterial biofilm[4].
|
-
-
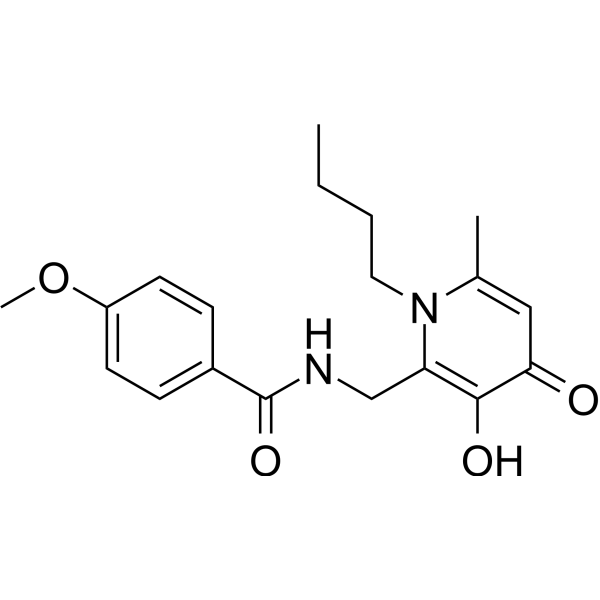
- HY-142695
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Antibacterial synergist 1 (compound 20P) is a bacterial biofilm inhibitor. Antibacterial synergist 1 inhibits the production of pyocyanin and biofilm formation with IC50s of 8.6 and 4.5 μM, respectively. Antibacterial synergist 1 has the potential for the research of P. aeruginosa infections .
|
-
-
- HY-N7788
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
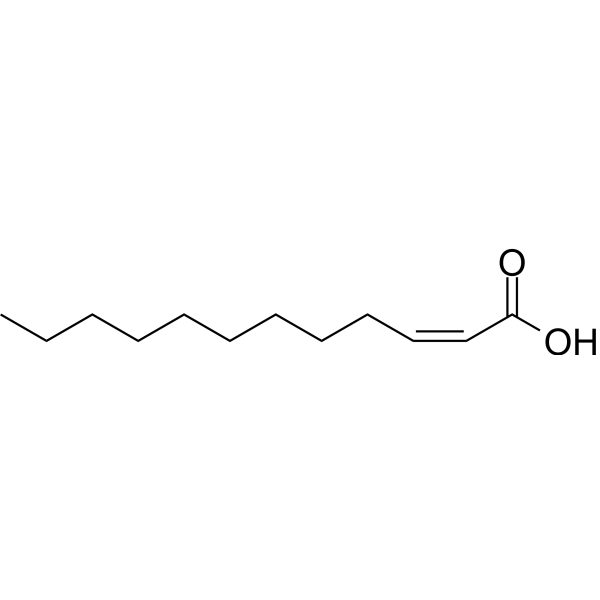
cis-2-Dodecenoic acid, originally discovered in Burkholderia cenocepacia, can interfere with the bacterial quorum sensing system and inhibit bacterial biofilm formation and virulence factor production .
|
-
-
- HY-155357
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
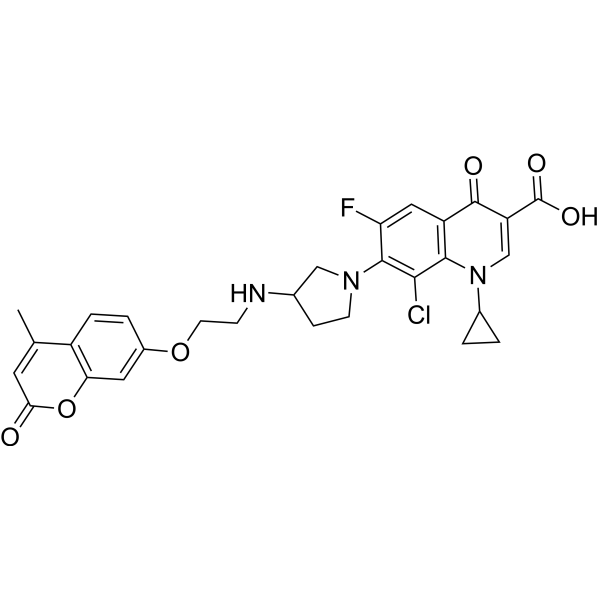
Antibacterial agent 160 is a potent antibacterial agents. Antibacterial agent 160 can rapidly kill bacterial and inhibits bacterial biofilm formation. Antibacterial agent 160 affects the normal function of DNA and leads cell death .
|
-
-
- HY-Y1093S2
-
|
Ethyl acetylacetate-d5
|
Bacterial
|
Others
|
|
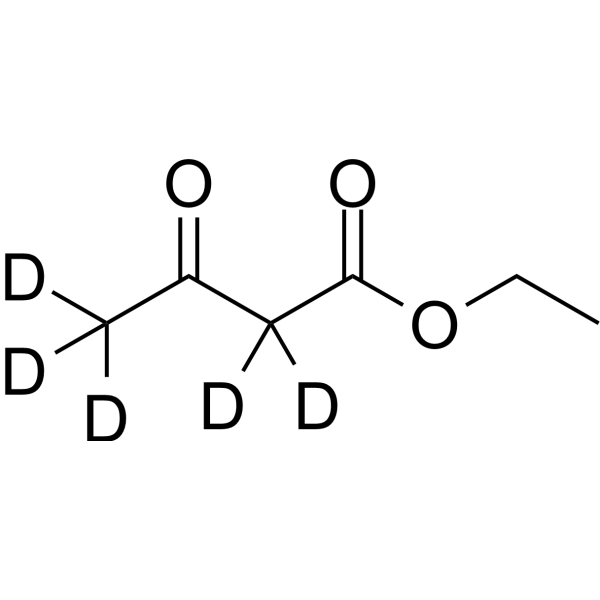
Ethyl acetoacetate-d5 is the deuterium labeled Ethyl acetoacetate[1]. Ethyl acetoacetate (Ethyl acetylacetate) is an ester widely used as an intermediate in the synthesis of many varieties of compounds[2][3][4]. Ethyl acetoacetate is an inhibitor of bacterial biofilm[5].
|
-
-
- HY-Y1093S3
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Others
|
|
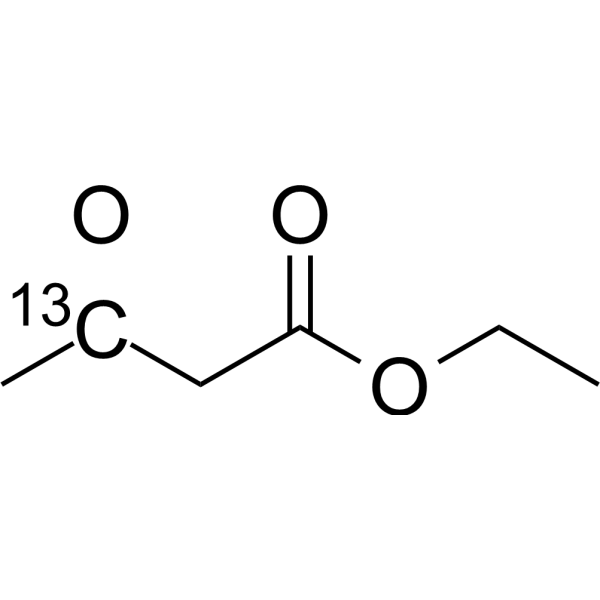
Ethyl acetoacetate- 13C is the 13C labeled Ethyl acetoacetate[1]. Ethyl acetoacetate (Ethyl acetylacetate) is an ester widely used as an intermediate in the synthesis of many varieties of compounds[2][3][4]. Ethyl acetoacetate is an inhibitor of bacterial biofilm[5].
|
-
-
- HY-Y1093S1
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Others
|
|
Ethyl acetoacetate- 13C4 is the 13C labeled Ethyl acetoacetate[1]. Ethyl acetoacetate (Ethyl acetylacetate) is an ester widely used as an intermediate in the synthesis of many varieties of compounds[2][3][4]. Ethyl acetoacetate is an inhibitor of bacterial biofilm[5].
|
-
-
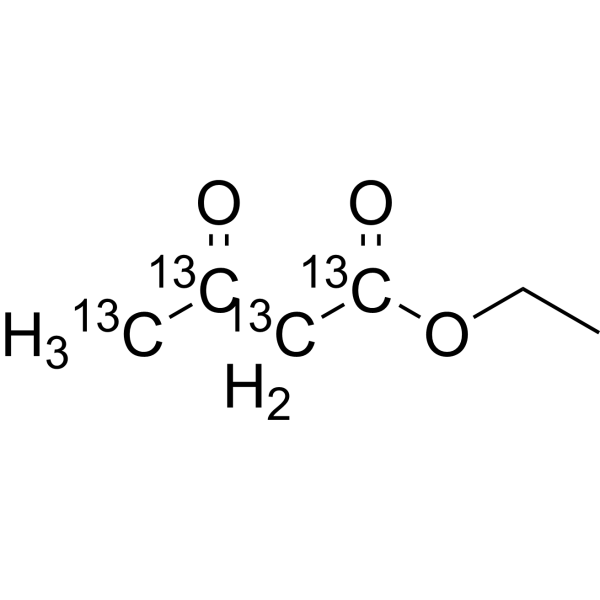
- HY-Y1093
-
|
Ethyl acetylacetate
|
|
|
|
Ethyl acetoacetate (Ethyl acetylacetate) is an ester widely used as an intermediate in the synthesis of many varieties of compounds . Ethyl acetoacetate is an inhibitor of bacterial biofilm .
|
-
-
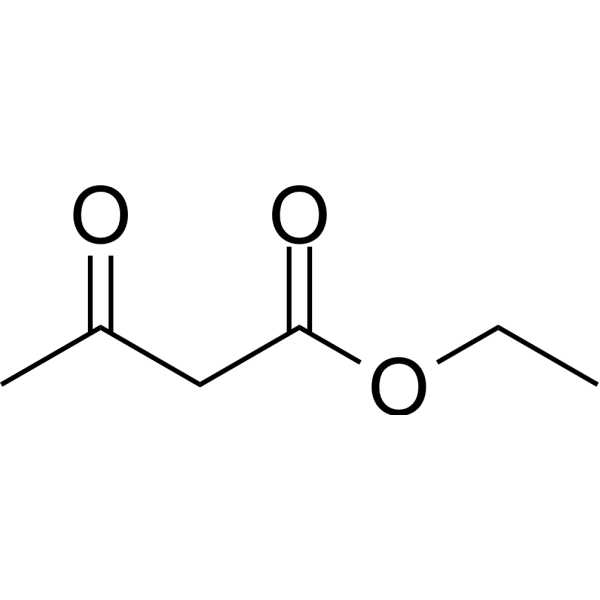
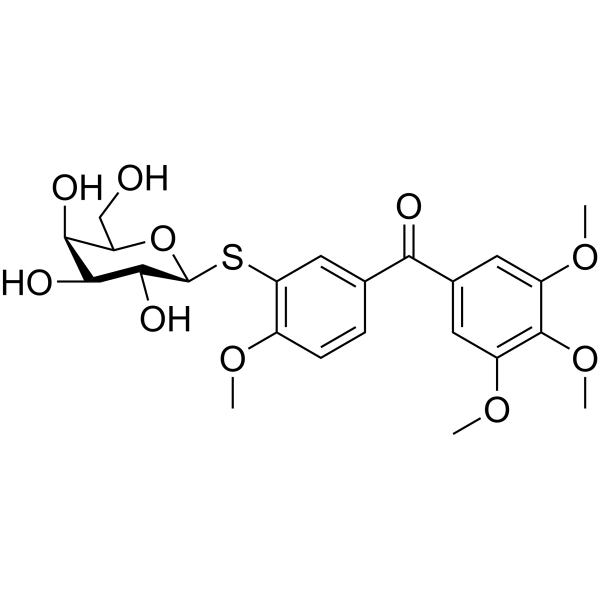
- HY-122950
-
|
|
Fungal
|
Infection
|
|
Harzianic acid, a tetramic acid derivative, with activity of antimicrobial, antibiofilm formation and biofilm disaggregation. Harzianic acid interferes with biofilm formation by limiting bacterial iron availability. Harzianic acid is also a selective inhibitor of Acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS), the first enzyme in the branched-chain amino acid biosynthetic pathway. Harzianic acid can used for herbicide and fungicide .
|
-
-
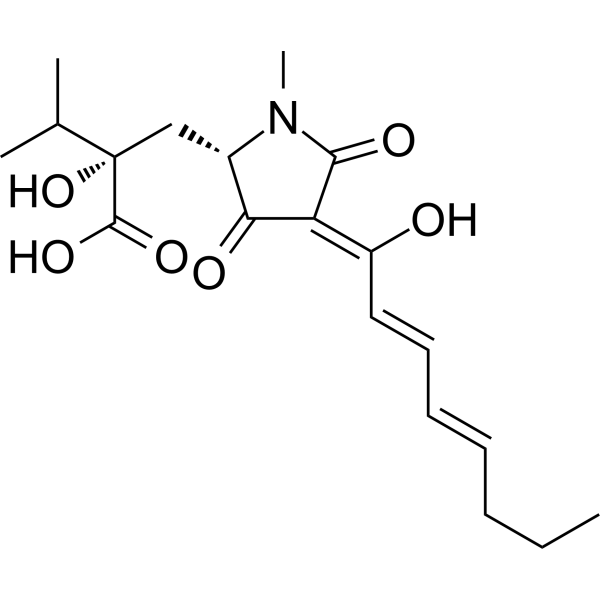
- HY-Y0444S
-
|
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Tyrosinase
|
|
|
D-Tyrosine-d2 is the deuterium labeled D-Tyrosine. D-Tyrosine is the D-isomer of tyrosine. D-Tyrosine negatively regulates melanin synthesis by inhibiting tyrosinase activity. D-Tyrosine inhibits biofilm formation and trigger the self-dispersal of biofilms without suppressing bacterial growth[1][2].
|
-
-
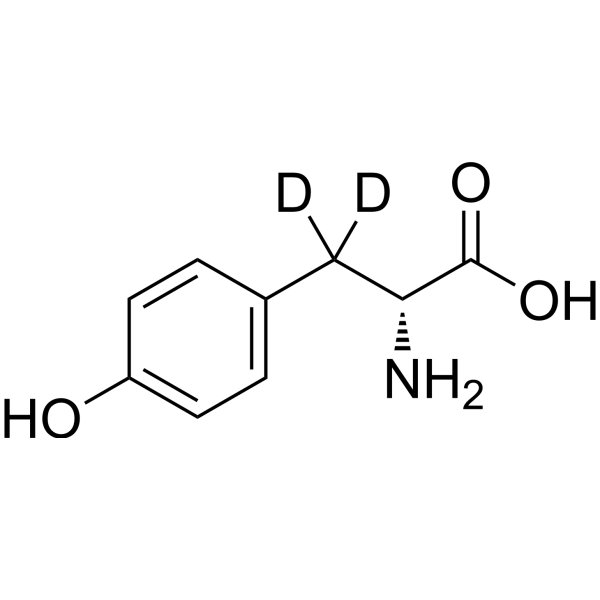
- HY-Y0444S1
-
|
|
Tyrosinase
|
|
|
D-Tyrosine-d4 is the deuterium labeled D-Tyrosine. D-Tyrosine is the D-isomer of tyrosine. D-Tyrosine negatively regulates melanin synthesis by inhibiting tyrosinase activity. D-Tyrosine inhibits biofilm formation and trigger the self-dispersal of biofilms without suppressing bacterial growth[1][2].
|
-
-
- HY-Y0444S2
-
|
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Tyrosinase
|
|
|
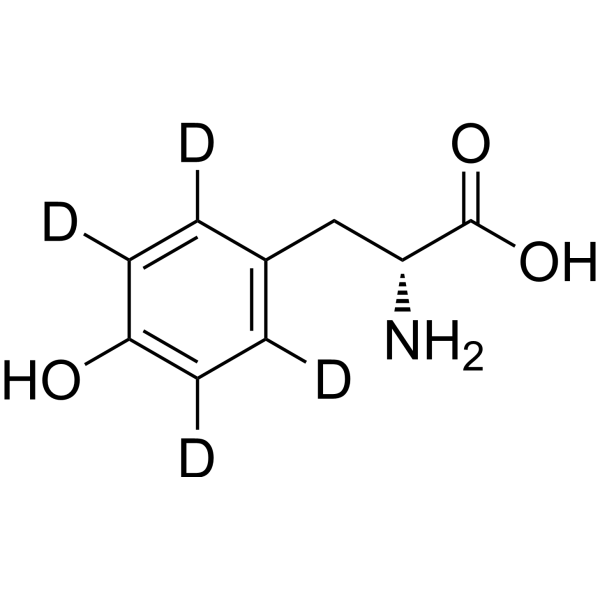
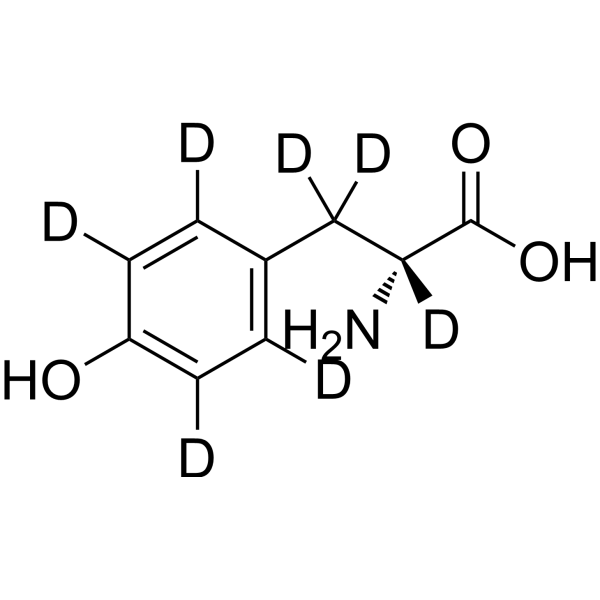
D-Tyrosine-d7 is the deuterium labeled D-Tyrosine. D-Tyrosine is the D-isomer of tyrosine. D-Tyrosine negatively regulates melanin synthesis by inhibiting tyrosinase activity. D-Tyrosine inhibits biofilm formation and trigger the self-dispersal of biofilms without suppressing bacterial growth[1][2].
|
-
-
- HY-Y1891
-
Tween 80
Maximum Cited Publications
41 Publications Verification
Polysorbate 80
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Tween 80 (Polysorbate 80), a surfactant, has been widely used as a solvent for pharmacological experiments. Tween 80 can also reduce bacterial attachment and inhibit biofilm formation.
|
-

-
- HY-131011
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
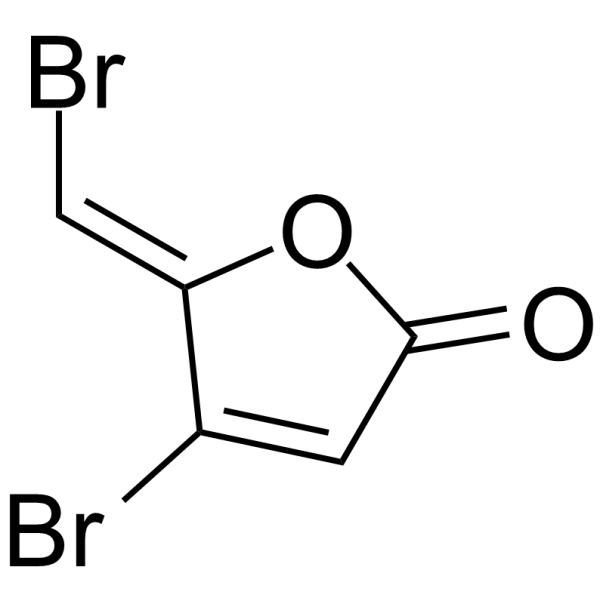
Furanone C-30 is a quorum sensing inhibitor. Furanone C-30 can effectively inhibit bacterial biofilm formation by S. mutans and its luxSmutant strain .
|
-
-
- HY-Y1718
-
|
N-Tridecanoic acid
|
Endogenous Metabolite
Bacterial
|
Infection
Metabolic Disease
|
|
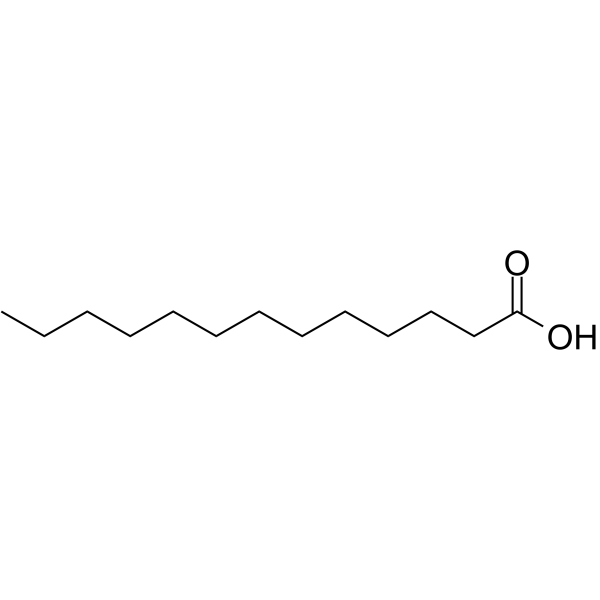
Tridecanoic acid (N-Tridecanoic acid), a 13-carbon medium-chain saturated fatty acid, can serve as an antipersister and antibiofilm agent that may be applied to research bacterial infections. Tridecanoic acid inhibits Escherichia coli persistence and biofilm formation .
|
-
-
- HY-147814
-
|
|
Bacterial
Fungal
|
Infection
|
|
KFU-127 (Compound 6b) is a broad spectrum topical antimicrobial capable of one-shot targeting of bacterial and fungal-bacterial biofilms. KFU-127 is considerably toxic for eukaryotic cells . KFU-127 is a click chemistry reagent, it contains an Alkyne group and can undergo copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAc) with molecules containing Azide groups.
|
-
-
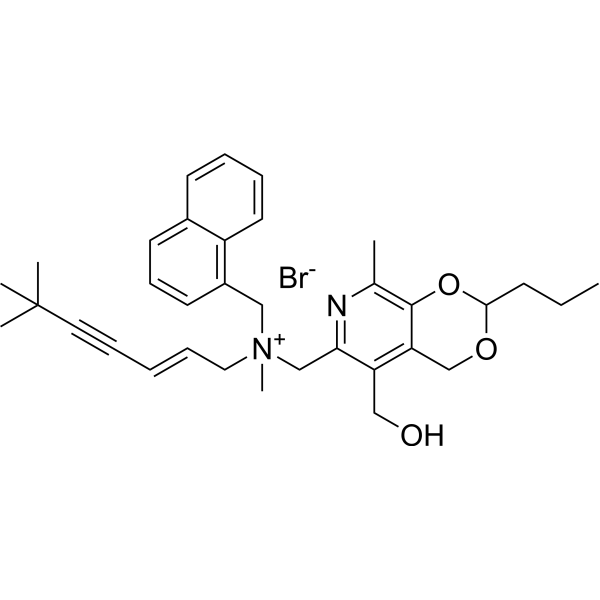
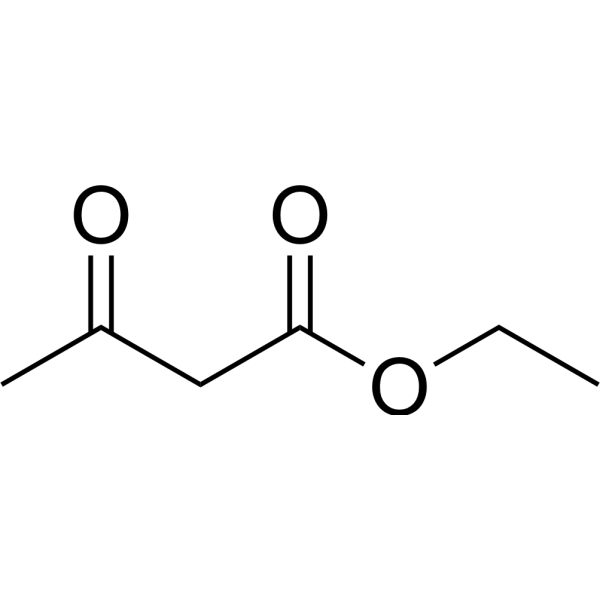
- HY-Y1093R
-
|
Ethyl acetylacetate (Standard)
|
Bacterial
|
Others
|
|
Ethyl acetoacetate (Standard) is the analytical standard of Ethyl acetoacetate. This product is intended for research and analytical applications. Ethyl acetoacetate (Ethyl acetylacetate) is an ester widely used as an intermediate in the synthesis of many varieties of compounds . Ethyl acetoacetate is an inhibitor of bacterial biofilm .
|
-
-
- HY-N2947
-
|
|
P-glycoprotein
|
Infection
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
Boeravinone B, a dual inhibitor of NorA bacterial efflux pump of Staphylococcus aureus and human P-Glycoprotein, reduces the biofilm formation and intracellular invasion of bacteria. Boeravinone B act as anti-aging and anti-apoptosis phyto-molecules during oxidative stress .
|
-
-
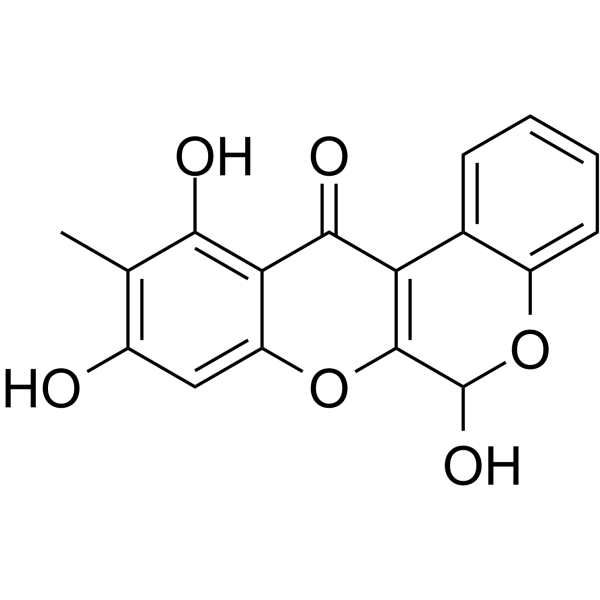
- HY-134215
-
|
|
Bacterial
Fungal
|
Infection
|
cis-11-Methyl-2-dodecenoic acid is a quorum sensing (QS) signal that acts as a diffusion signaling factor (DSF) in extracellular microbial and fungal communication systems. DSF is involved in the regulation of virulence and biofilm formation of a variety of bacterial pathogens .
|
-
-
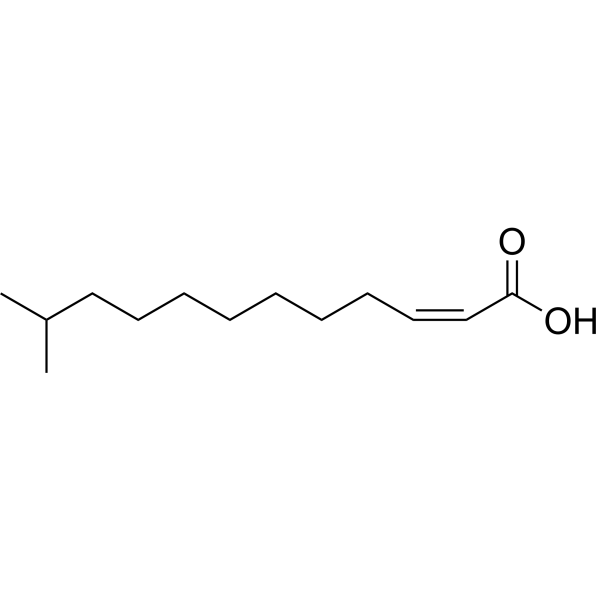
- HY-P5681
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
Human α-Defensin 6, a 32-residue cysteine-rich peptide, can inhibit bacterial invasion and contribute to the mucosal immunity. Human α-Defensin 6 forms ordered self-assembly fibrils and nanonets that surround and entangle bacteria after stochastic binding to bacterial surface proteins. Human α-Defensin 6 also inhibits C. albicans biofilm formation .
|
-

-
- HY-W001132
-
Indole
1 Publications Verification
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Infection
|
|
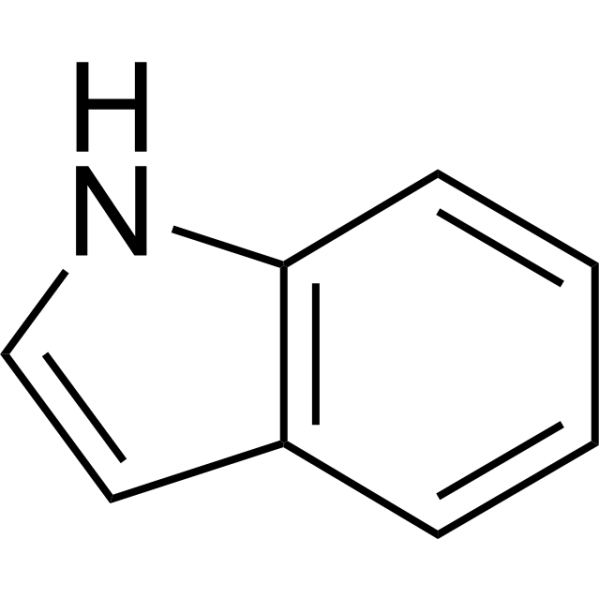
Indole is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound which widely distributed in the natural environment and can be produced by a variety of bacteria. Indole regulates various aspects of bacterial physiology, including spore formation, plasmid stability, resistance to drugs, biofilm formation, and virulence as an intercellular signal molecule .
|
-
-
- HY-107780
-
|
c-di-GMP; cyclic diguanylate; 5GP-5GP
|
STING
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Cancer
|
|
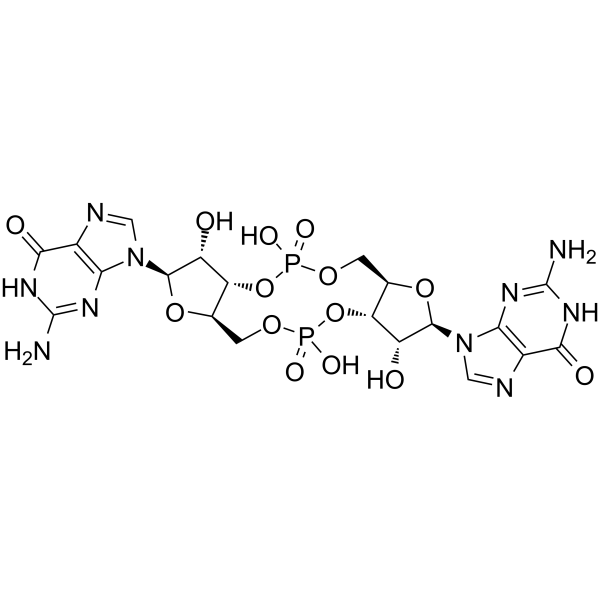
Cyclic-di-GMP is a STING agonist and a bacterial second messenger that coordinates different aspects of bacterial growth and behavior, including motility, virulence, biofilm formation, and cell cycle progression. Cyclic-di-GMP has anti-cancer cell proliferation activity and also induces elevated CD4 receptor expression and cell cycle arrest. Cyclic-di-GMP can be used in cancer research .
|
-
-
- HY-107780A
-
|
c-di-GMP sodium; cyclic diguanylate sodium; 5GP-5GP sodium
|
STING
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Cancer
|
|
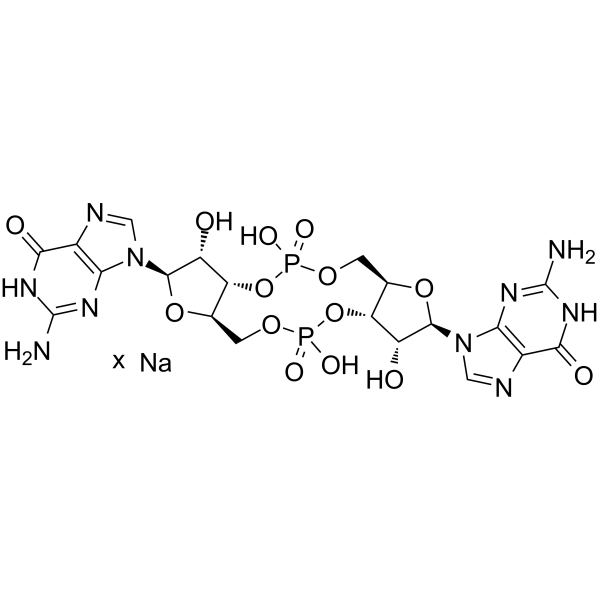
Cyclic-di-GMP sodium is a STING agonist and a bacterial second messenger that coordinates different aspects of bacterial growth and behavior, including motility, virulence, biofilm formation, and cell cycle progression. Cyclic-di-GMP sodium has anti-cancer cell proliferation activity and also induces elevated CD4 receptor expression and cell cycle arrest. Cyclic-di-GMP sodium can be used in cancer research .
|
-
-
- HY-107780B
-
|
c-di-GMP diammonium; cyclic diguanylate diammonium; 5GP-5GP diammonium
|
STING
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Cancer
|
|
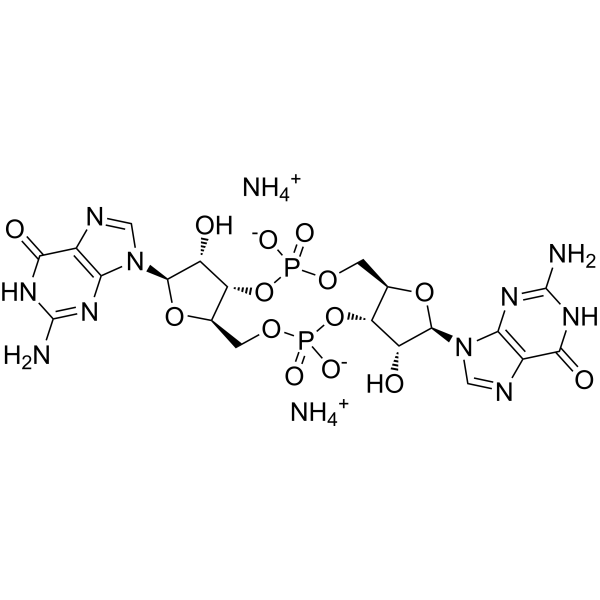
Cyclic-di-GMP diammonium is a STING agonist and a bacterial second messenger that coordinates different aspects of bacterial growth and behavior, including motility, virulence, biofilm formation, and cell cycle progression. Cyclic-di-GMP diammonium has anti-cancer cell proliferation activity and also induces elevated CD4 receptor expression and cell cycle arrest. Cyclic-di-GMP diammonium can be used in cancer research .
|
-
-
- HY-110382
-
|
c-di-GMP disodium; cyclic diguanylate disodium; 5GP-5GP disodium
|
STING
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Cancer
|
|
Cyclic-di-GMP disodium is a STING agonist and a bacterial second messenger that coordinates different aspects of bacterial growth and behavior, including motility, virulence, biofilm formation, and cell cycle progression. Cyclic-di-GMP disodium has anti-cancer cell proliferation activity and also induces elevated CD4 receptor expression and cell cycle arrest. Cyclic-di-GMP disodium can be used in cancer research .
|
-
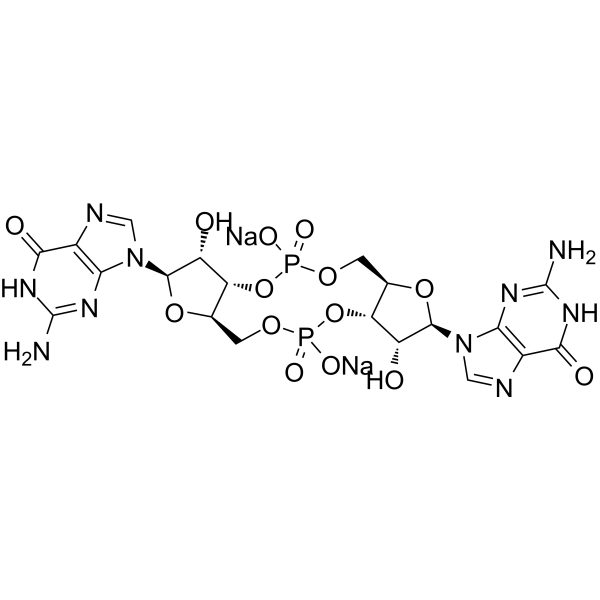
-
- HY-Y1718S
-
|
N-Tridecanoic acid-d2
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Endogenous Metabolite
Bacterial
|
|
|
Tridecanoic acid-d2 is the deuterium labeled Tridecanoic acid. Tridecanoic acid (N-Tridecanoic acid), a 13-carbon medium-chain saturated fatty acid, can serve as an antipersister and antibiofilm agent that may be applied to research bacterial infections. Tridecanoic acid inhibits Escherichia coli persistence and biofilm formation[1].
|
-
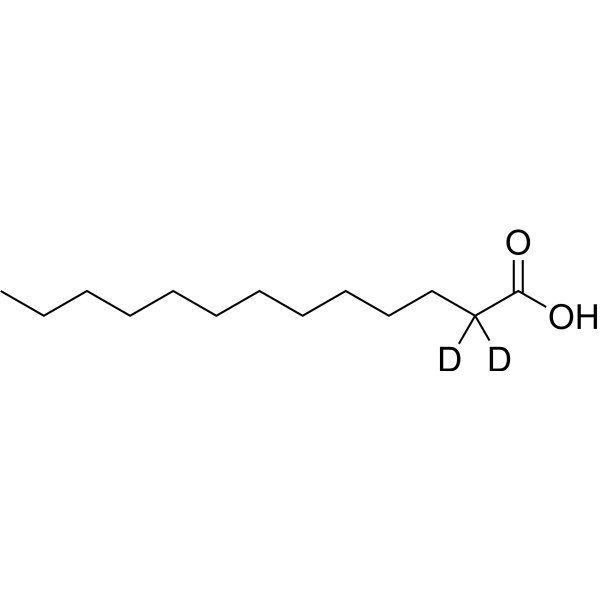
-
- HY-Y1718S1
-
|
N-Tridecanoic acid-d25
|
Endogenous Metabolite
Bacterial
|
Cancer
|
|
Tridecanoic acid-d25 is the deuterium labeled Tridecanoic acid. Tridecanoic acid (N-Tridecanoic acid), a 13-carbon medium-chain saturated fatty acid, can serve as an antipersister and antibiofilm agent that may be applied to research bacterial infections. Tridecanoic acid inhibits Escherichia coli persistence and biofilm formation[1].
|
-
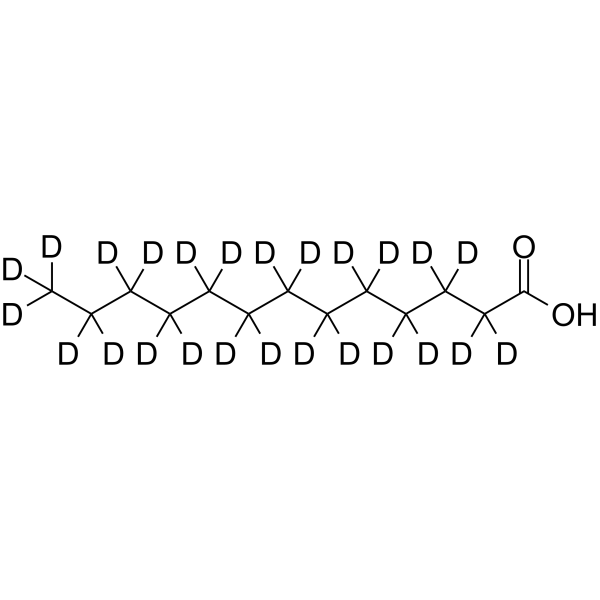
-
- HY-Y1718S2
-
|
N-Tridecanoic acid-d9
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Endogenous Metabolite
Bacterial
|
|
|
Tridecanoic acid-d9 is the deuterium labeled Tridecanoic acid. Tridecanoic acid (N-Tridecanoic acid), a 13-carbon medium-chain saturated fatty acid, can serve as an antipersister and antibiofilm agent that may be applied to research bacterial infections. Tridecanoic acid inhibits Escherichia coli persistence and biofilm formation[1].
|
-
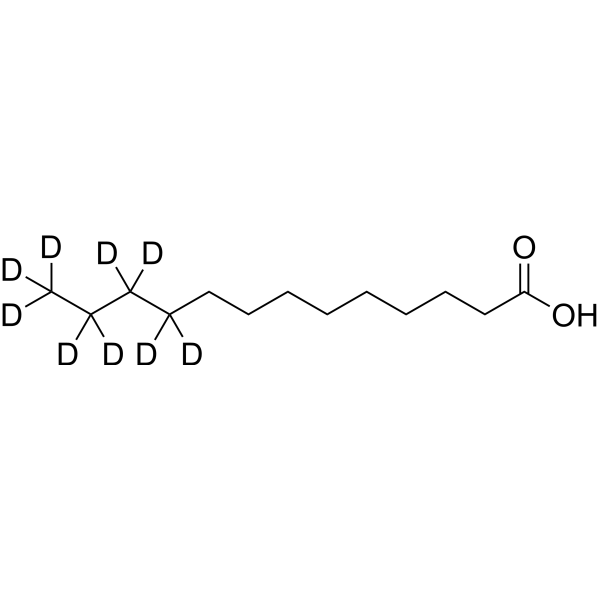
-
- HY-P4370
-
|
|
Bacterial
Fungal
|
Infection
|
|
Hepcidin-20 (human) is a histidine-containing, cysteine-rich, β-sheet structured peptide. Hepcidin-20 (human) shows antifungal activity. Hepcidin-20 (human) inhibits biofilm formation and bacterial cell metabolism of polysaccharide intercellular adhesin (PIA)-positive and PIA-negative strains .
|
-
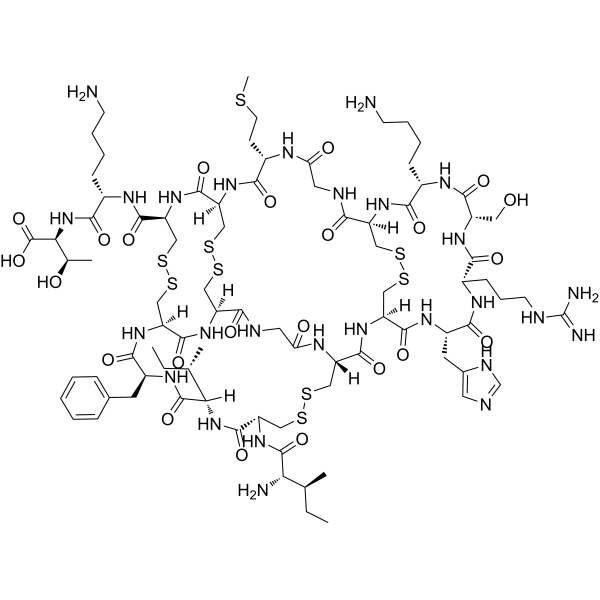
-
- HY-155461
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Antibiofilm agent-3 (compound 3b) is a tetracarboxamide antibacterial agent that effectively inhibits the plant bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas citri (Xanthomonas citri ssp. citri, Xcc) (MIC=500 μg/ mL). Antibiofilm agent-3 inhibits biofilm formation by Xcc with IC50=15.37 μg/mL .
|
-
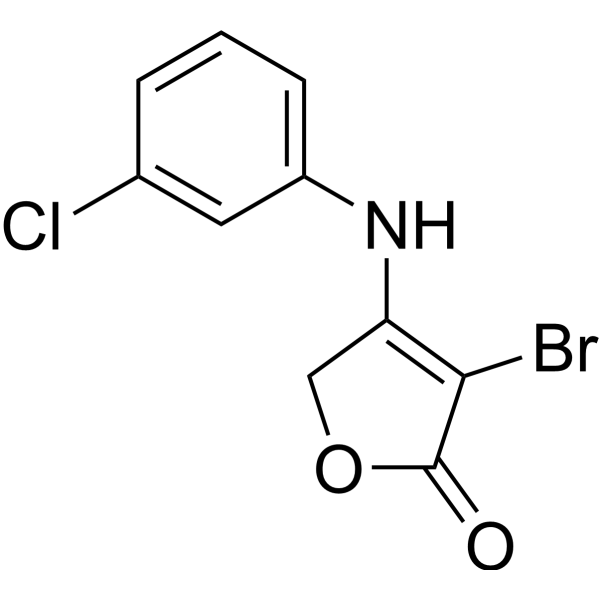
-
- HY-152175
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Antibacterial agent 130 is a 1,1-diarylthiogalactoside, used for targeting the Pseudomonas aeruginosa LecA. Antibacterial agent 130 shows high affinity toward LecA (Kd=1 μM). Antibacterial agent 130 has antibiofilm activity, but lacks bactericidal activity. LecA, a lectin and virulence factor from Pseudomonas aeruginosa involved in bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation .
|
-
-
- HY-P5706
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
HG2 is a fast-acting antimicrobial peptide. HG2 shows anti-biofilm and anti-inflammatory activities. HG2 is active against Gram-positive pathogens, especially against MRSA strains (MIC: 16-32?μg/mL). HG2 can bind to bacterial lipids and reduces ATP concentration in S. aureus MRSA USA300 cells .
|
-
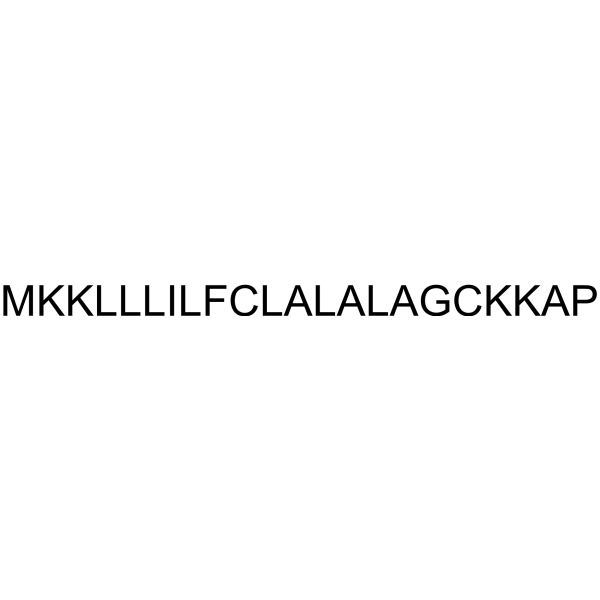
-
- HY-P5709
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
HG4 is a fast-acting antimicrobial peptide. HG4 shows anti-biofilm and anti-inflammatory activities. HG4 is active against Gram-positive pathogens, especially against MRSA strains (MIC: 32-64?μg/mL). HG4 can bind to bacterial lipids and reduces ATP concentration in S. aureus MRSA USA300 cells .
|
-
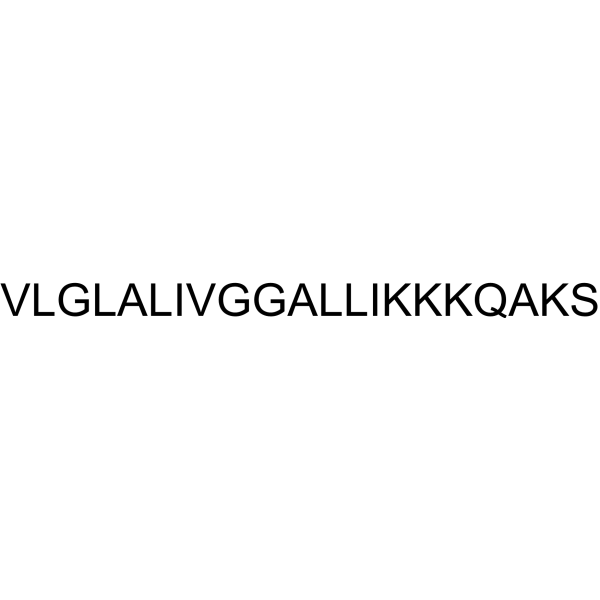
-
- HY-149734
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
MA220607 is an antibacterial agent with low hemolytic toxicity and a dual-target mechanism of action (MOA). MA220607 promotes FtsZ protein polymerization, also increases the permeability of bacterial membranes and inhibits biofilm formation. The resistance rate of MA220607 is low, and the MICs against Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria are Table 0.062-2 μg/mL and 0.5-4 μg/mL, respectively) .
|
-
-
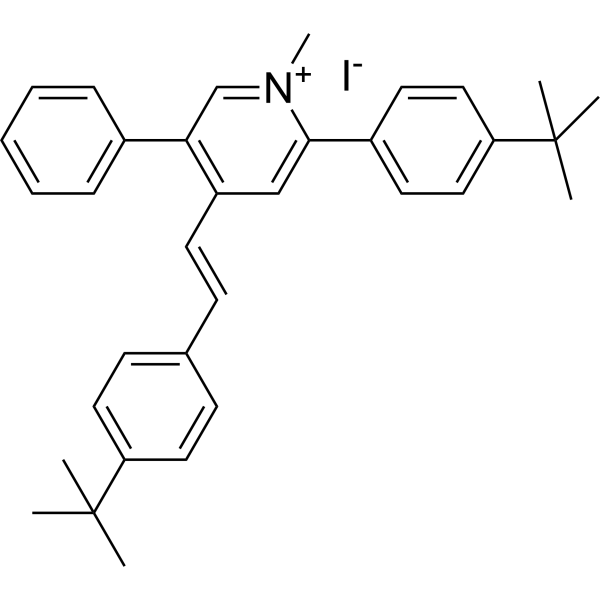
- HY-161279
-
|
|
Bacterial
Lactate Dehydrogenase
Reactive Oxygen Species
|
Infection
|
|
Antibiofilm agent-5 (compound 6c) is a multitargeting antibacterial agent with potent antibiofilm activity. Antibiofilm agent-5 could induce metabolic dysfunction by deactivating lactate dehydrogenase and promote the accumulation of reactive oxygen species to decrease the reduced glutathione and ultimately cause oxidative damage in bacteria. Antibiofilm agent-5 can be used for the research of refractory biofilm-intensified bacterial infections .
|
-
-
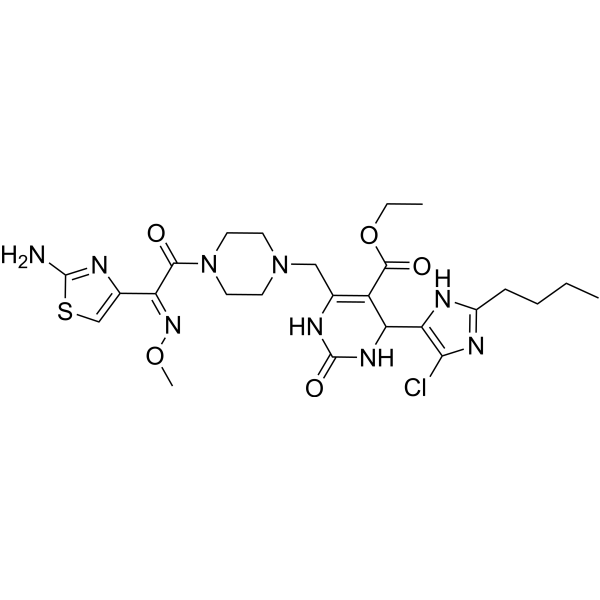
- HY-161395
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
IDD-8E is an effective anti-pseudomonal agent (MIC =4.4 µM ) with no cytotoxicity. IDD-8E shows significant pseudomonal killing and disruption of pseudomonal biofilm. IDD-8E binds to the ATP-binding pocket of WaaP and also inhibits other ESKAPE pathogens.
|
-
-
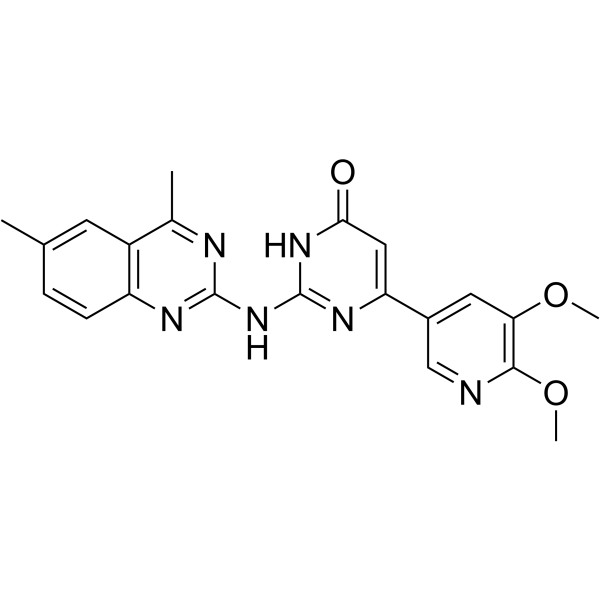
- HY-P5704
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
K11 is an antimicrobial peptide. K11 is active against MDR/XDR K. pneumoniae isolates (MIC: 8-512 μg/mL), and inhibits bacterial biofilm formation. K11 can act synergistically with antibiotics (Chloramphenicol (HY-B0239), Meropenem (HY-13678), Rifampicin (HY-B0272), etc.) against drug-resistant K. pneumoniae. K11 has high thermal and wide pH stability .
|
-
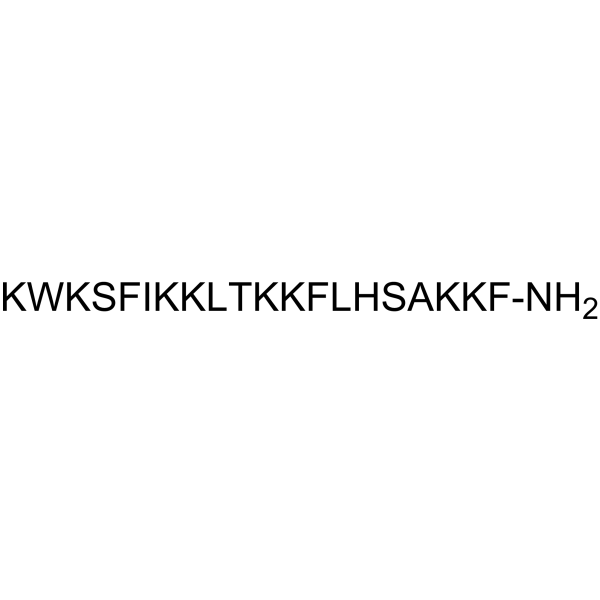
-
- HY-155479
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
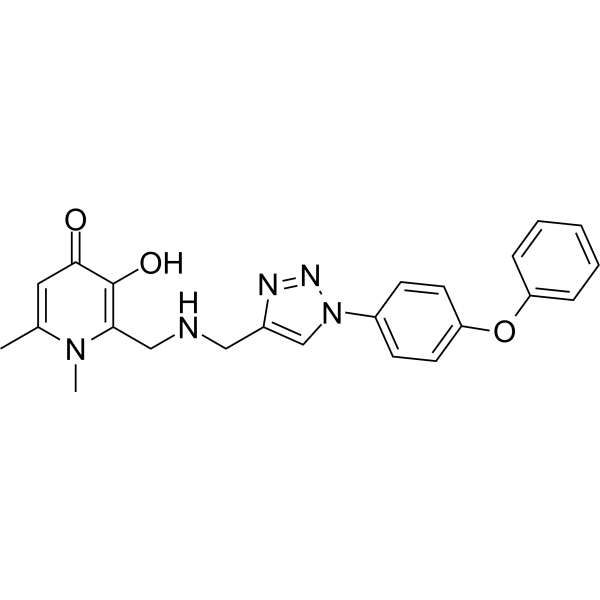
PqsR-IN-3 (compound 16e) is a selective inhibitor of the pqs system (IC50=3.7 μM) and its associated virulence factor pyocyanin (IC50=2.7 μM). PqsR-IN-3 inhibits bacterial biofilm synthesis and is significantly cytotoxic against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PqsR-IN-3 has synergistic effects with several antibiotics, such as Ciprofloxacin (HY-B0356) and Tobramycin (HY-B0441) .
|
-
-
- HY-W127487
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
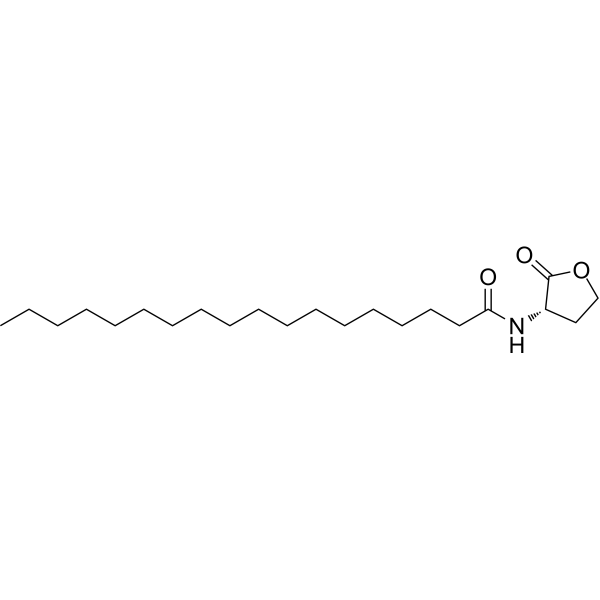
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria to control gene expression in response to increased cell density. This regulatory process manifests itself in a variety of phenotypes, including biofilm formation and virulence factor production. Coordinated gene expression is achieved through the production, release and detection of small diffusible signaling molecules called autoinducers. N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise a class of such autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled to a homoserine lactone (HSL). Modulation of bacterial quorum-sensing signaling systems to suppress pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial research for infectious diseases. AHLs differ in acyl length (C4-C18), C3 substitution (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signaling specificity through the affinity of the LuxR family of transcriptional regulators. C18-HSL, one of four lipophilic long acyl side chain AHLs produced by the LuxI AHL synthase homolog SinI, is involved in quorum-sensing signaling in strains of Rhizobium meliloti (a nitrogen-fixing bacterial symbiont of the legume M. sativa) . C18-HSL and other hydrophobic AHLs tend to localize in the relatively lipophilic environment of bacterial cells and cannot diffuse freely across the cell membrane. Long-chain N-acyl homoserine lactones can be exported from cells by efflux pumps, or can be transported between communicating cells by extracellular outer membrane vesicles.
|
-
-
- HY-114773
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
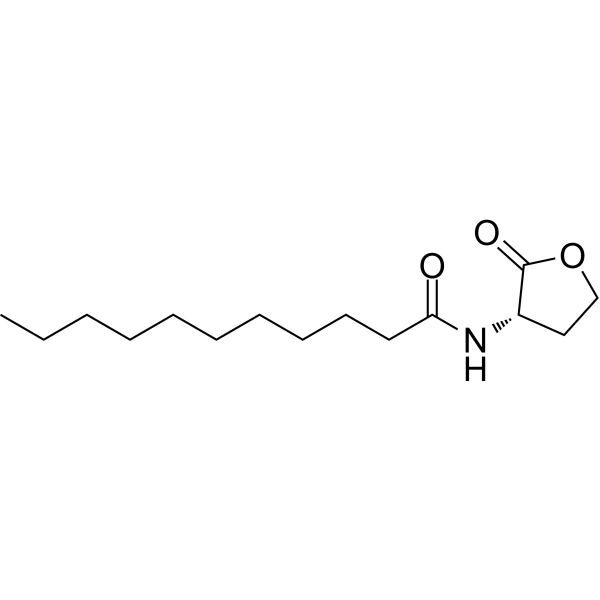
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria to control gene expression in response to increased cell density. This regulatory process manifests itself in a variety of phenotypes, including biofilm formation and virulence factor production. Coordinated gene expression is achieved through the production, release and detection of small diffusible signaling molecules called autoinducers. N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise a class of such autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled to a homoserine lactone (HSL). Modulation of bacterial quorum-sensing signaling systems to suppress pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial research for infectious diseases. AHLs differ in acyl length (C4-C18), C3 substitution (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signaling specificity through the affinity of the LuxR family of transcriptional regulators. C11-HSL has a rare odd-numbered acyl carbon chain and may be a minor quorum-sensing signaling molecule in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains.
|
-
-
- HY-W127393
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria to control gene expression in response to increased cell density. This regulatory process manifests itself in a variety of phenotypes, including biofilm formation and virulence factor production. Coordinated gene expression is achieved through the production, release and detection of small diffusible signaling molecules called autoinducers. N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise a class of such autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled to a homoserine lactone (HSL). Modulation of bacterial quorum-sensing signaling systems to suppress pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial research for infectious diseases. AHLs differ in acyl length (C4-C18), C3 substitution (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signaling specificity through the affinity of the LuxR family of transcriptional regulators. C9-HSL is a rare odd-numbered acyl carbon chain produced by wild-type Erwinia carotovora strain SCC 3193 grown in nutrient-rich Luria-Bertani broth (LB) medium.
|
-
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Type |
-
- HY-Y1891
-
|
Polysorbate 80
|
Co-solvents
|
|
Tween 80 (Polysorbate 80), a surfactant, has been widely used as a solvent for pharmacological experiments. Tween 80 can also reduce bacterial attachment and inhibit biofilm formation.
|
-
- HY-W127487
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria to control gene expression in response to increased cell density. This regulatory process manifests itself in a variety of phenotypes, including biofilm formation and virulence factor production. Coordinated gene expression is achieved through the production, release and detection of small diffusible signaling molecules called autoinducers. N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise a class of such autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled to a homoserine lactone (HSL). Modulation of bacterial quorum-sensing signaling systems to suppress pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial research for infectious diseases. AHLs differ in acyl length (C4-C18), C3 substitution (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signaling specificity through the affinity of the LuxR family of transcriptional regulators. C18-HSL, one of four lipophilic long acyl side chain AHLs produced by the LuxI AHL synthase homolog SinI, is involved in quorum-sensing signaling in strains of Rhizobium meliloti (a nitrogen-fixing bacterial symbiont of the legume M. sativa) . C18-HSL and other hydrophobic AHLs tend to localize in the relatively lipophilic environment of bacterial cells and cannot diffuse freely across the cell membrane. Long-chain N-acyl homoserine lactones can be exported from cells by efflux pumps, or can be transported between communicating cells by extracellular outer membrane vesicles.
|
-
- HY-114773
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria to control gene expression in response to increased cell density. This regulatory process manifests itself in a variety of phenotypes, including biofilm formation and virulence factor production. Coordinated gene expression is achieved through the production, release and detection of small diffusible signaling molecules called autoinducers. N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise a class of such autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled to a homoserine lactone (HSL). Modulation of bacterial quorum-sensing signaling systems to suppress pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial research for infectious diseases. AHLs differ in acyl length (C4-C18), C3 substitution (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signaling specificity through the affinity of the LuxR family of transcriptional regulators. C11-HSL has a rare odd-numbered acyl carbon chain and may be a minor quorum-sensing signaling molecule in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains.
|
-
- HY-W127393
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria to control gene expression in response to increased cell density. This regulatory process manifests itself in a variety of phenotypes, including biofilm formation and virulence factor production. Coordinated gene expression is achieved through the production, release and detection of small diffusible signaling molecules called autoinducers. N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise a class of such autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled to a homoserine lactone (HSL). Modulation of bacterial quorum-sensing signaling systems to suppress pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial research for infectious diseases. AHLs differ in acyl length (C4-C18), C3 substitution (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signaling specificity through the affinity of the LuxR family of transcriptional regulators. C9-HSL is a rare odd-numbered acyl carbon chain produced by wild-type Erwinia carotovora strain SCC 3193 grown in nutrient-rich Luria-Bertani broth (LB) medium.
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Area |
-
- HY-W141788
-
|
|
Peptides
|
Infection
|
|
N-Butyryl-DL-homocysteine thiolactone is an N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) analogue. AHLs are potent inhibitors of biofilm formation and virulence factors, and has been used for degrading microbial communities, reducing bacterial pathogenicity .
|
-
- HY-P5681
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
Human α-Defensin 6, a 32-residue cysteine-rich peptide, can inhibit bacterial invasion and contribute to the mucosal immunity. Human α-Defensin 6 forms ordered self-assembly fibrils and nanonets that surround and entangle bacteria after stochastic binding to bacterial surface proteins. Human α-Defensin 6 also inhibits C. albicans biofilm formation .
|
-
- HY-P4370
-
|
|
Bacterial
Fungal
|
Infection
|
|
Hepcidin-20 (human) is a histidine-containing, cysteine-rich, β-sheet structured peptide. Hepcidin-20 (human) shows antifungal activity. Hepcidin-20 (human) inhibits biofilm formation and bacterial cell metabolism of polysaccharide intercellular adhesin (PIA)-positive and PIA-negative strains .
|
-
- HY-P5706
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
HG2 is a fast-acting antimicrobial peptide. HG2 shows anti-biofilm and anti-inflammatory activities. HG2 is active against Gram-positive pathogens, especially against MRSA strains (MIC: 16-32?μg/mL). HG2 can bind to bacterial lipids and reduces ATP concentration in S. aureus MRSA USA300 cells .
|
-
- HY-P5709
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
HG4 is a fast-acting antimicrobial peptide. HG4 shows anti-biofilm and anti-inflammatory activities. HG4 is active against Gram-positive pathogens, especially against MRSA strains (MIC: 32-64?μg/mL). HG4 can bind to bacterial lipids and reduces ATP concentration in S. aureus MRSA USA300 cells .
|
-
- HY-P5704
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
K11 is an antimicrobial peptide. K11 is active against MDR/XDR K. pneumoniae isolates (MIC: 8-512 μg/mL), and inhibits bacterial biofilm formation. K11 can act synergistically with antibiotics (Chloramphenicol (HY-B0239), Meropenem (HY-13678), Rifampicin (HY-B0272), etc.) against drug-resistant K. pneumoniae. K11 has high thermal and wide pH stability .
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Category |
Target |
Chemical Structure |
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-Y1093S4
-
|
|
|
Ethyl acetoacetate-d3 is the deuterium labeled Ethyl acetoacetate. Ethyl acetoacetate (Ethyl acetylacetate) is an ester widely used as an intermediate in the synthesis of many varieties of compounds[1][2][3]. Ethyl acetoacetate is an inhibitor of bacterial biofilm[4].
|
-

-
- HY-Y1093S2
-
|
|
|
Ethyl acetoacetate-d5 is the deuterium labeled Ethyl acetoacetate[1]. Ethyl acetoacetate (Ethyl acetylacetate) is an ester widely used as an intermediate in the synthesis of many varieties of compounds[2][3][4]. Ethyl acetoacetate is an inhibitor of bacterial biofilm[5].
|
-

-
- HY-Y1093S3
-
|
|
|
Ethyl acetoacetate- 13C is the 13C labeled Ethyl acetoacetate[1]. Ethyl acetoacetate (Ethyl acetylacetate) is an ester widely used as an intermediate in the synthesis of many varieties of compounds[2][3][4]. Ethyl acetoacetate is an inhibitor of bacterial biofilm[5].
|
-

-
- HY-Y1093S1
-
|
|
|
Ethyl acetoacetate- 13C4 is the 13C labeled Ethyl acetoacetate[1]. Ethyl acetoacetate (Ethyl acetylacetate) is an ester widely used as an intermediate in the synthesis of many varieties of compounds[2][3][4]. Ethyl acetoacetate is an inhibitor of bacterial biofilm[5].
|
-

-
- HY-Y0444S
-
|
|
|
D-Tyrosine-d2 is the deuterium labeled D-Tyrosine. D-Tyrosine is the D-isomer of tyrosine. D-Tyrosine negatively regulates melanin synthesis by inhibiting tyrosinase activity. D-Tyrosine inhibits biofilm formation and trigger the self-dispersal of biofilms without suppressing bacterial growth[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-Y0444S1
-
|
|
|
D-Tyrosine-d4 is the deuterium labeled D-Tyrosine. D-Tyrosine is the D-isomer of tyrosine. D-Tyrosine negatively regulates melanin synthesis by inhibiting tyrosinase activity. D-Tyrosine inhibits biofilm formation and trigger the self-dispersal of biofilms without suppressing bacterial growth[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-Y0444S2
-
|
|
|
D-Tyrosine-d7 is the deuterium labeled D-Tyrosine. D-Tyrosine is the D-isomer of tyrosine. D-Tyrosine negatively regulates melanin synthesis by inhibiting tyrosinase activity. D-Tyrosine inhibits biofilm formation and trigger the self-dispersal of biofilms without suppressing bacterial growth[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-Y1718S
-
|
|
|
Tridecanoic acid-d2 is the deuterium labeled Tridecanoic acid. Tridecanoic acid (N-Tridecanoic acid), a 13-carbon medium-chain saturated fatty acid, can serve as an antipersister and antibiofilm agent that may be applied to research bacterial infections. Tridecanoic acid inhibits Escherichia coli persistence and biofilm formation[1].
|
-

-
- HY-Y1718S1
-
|
|
|
Tridecanoic acid-d25 is the deuterium labeled Tridecanoic acid. Tridecanoic acid (N-Tridecanoic acid), a 13-carbon medium-chain saturated fatty acid, can serve as an antipersister and antibiofilm agent that may be applied to research bacterial infections. Tridecanoic acid inhibits Escherichia coli persistence and biofilm formation[1].
|
-
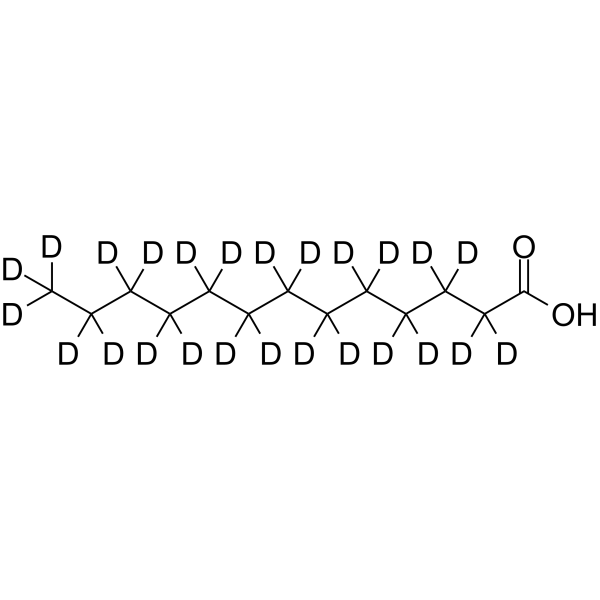
-
- HY-Y1718S2
-
|
|
|
Tridecanoic acid-d9 is the deuterium labeled Tridecanoic acid. Tridecanoic acid (N-Tridecanoic acid), a 13-carbon medium-chain saturated fatty acid, can serve as an antipersister and antibiofilm agent that may be applied to research bacterial infections. Tridecanoic acid inhibits Escherichia coli persistence and biofilm formation[1].
|
-

Your information is safe with us. * Required Fields.
Inquiry Information
- Product Name:
- Cat. No.:
- Quantity:
- MCE Japan Authorized Agent: